The essential component of effective CPR is the compression-to-ventilation ratio, which varies based on the patient's age and specific circumstances.
Perform 30 chest compressions followed by 2 rescue breaths.
Use two fingers for gentle compressions.
One rescuer does compressions while the other gives breaths.
Alternate 15 compressions with 2 breaths.
Adjust hand placement & compression force for pregnant individuals, the elderly, or those with specific medical conditions. If unable to provide rescue breaths, focus on hands-on CPR (continuous chest compressions).
The CPR ratio for adults is the number of rescue breaths and chest compressions during cardiopulmonary resuscitation. This includes providing chest compressions at the correct rate and depth. Let us take a look at the ventilation ratio:
Compression to Ventilation Ratio
The compression-to ventilation ratio is the number of chest compressions followed by the number of breaths given during CPR. The correct ratio for adults is 30:2, meaning 30 chest compressions are followed by 2 rescue breaths. This maintains a steady rhythm in the heart.
Rate of Compressions
The correct rate of CPR compression for adults is 100–120 compressions every minute. This rate refers to how fast chest compressions are given. For instance, 100 compressions per minute means giving 100 compressions within a minute if no ventilation is required.
Depth of Compressions
For adults, the compression depth should be 2 to 2.4 inches (5 to 6 cm), with a rate of 100–120 compressions per minute. This depth means how far the victim’s chest is pressed down with each compression. It's crucial to allow the chest to recoil between every compression fully.
Rescue Breathing for Adults
Rescue breathing is the number of breaths administered per minute. For adults, this should be 10–12 breaths per minute. Each breath should last one second and be enough to make the chest rise. When using a bag valve mask (BVM), deliver 500 ml of air with each breath. For an AED (Automated External Defibrillator), you can alternate between 34 shocks along with performing CPR for one minute.
The CPR ratio for adults is the number of rescue breaths and chest compressions during cardiopulmonary resuscitation. This includes providing chest compressions at the correct rate and depth. Let us take a look at the ventilation ratio:
Compression to Ventilation Ratio
The child compression-to-ventilation ratio is 30:2, which is the same for adults. This means performing 30 chest compressions, which are followed by two rescue breaths. In cases where there are two rescuers, the compression ratio shifts to 15:2.
Rate of Compressions
For children, aim for a CPR compression rate of at least 100 to 120 beats per minute. Once you are done performing 30 compressions, remember to tilt the head, lift the chin, and deliver two effective breaths. Although the target CPR compression rate is 100–120 per minute, interruptions between the breaths can result in a lower count.
Depth of Compressions
During pediatric CPR, ensure the compression depth reaches at least one-third of the chest diameter, which is around 2 inches or 5 cm. Then keep a steady compression rate of 100–120 per minute for optimal effectiveness. Maintaining these guidelines is vital to delivering effective chest compressions to children in need.
Rescue Breathing for Adults
To administer rescue breathing to a child, start by placing one hand on the child's forehead and gently tilting the head back using your palm. Next, take a normal breath and deliver it into the child's mouth for 1 second. Look carefully to ensure the child's chest rises with each breath.
When infants are unconscious, unresponsive, or not breathing, CPR is crucial. It ensures oxygenated blood keeps flowing through their bodies with proper chest compressions and rescue breathing until advanced medical assistance arrives. Let us understand infant CPR better.
Compression to Ventilation Ratio
Infants follow the same compression-to-ventilation ratio as adults and children, which is 30 compressions to 2 breaths. This means giving 30 chest compressions, followed by two rescue breaths. In the case of two rescuers, the ratio changes to 15 compressions to 2 breaths.
Rate of Compressions
The correct rate of compression for infants is around 100 to 120 compressions per minute. The rescuer should perform 100 to 120 chest compressions. As infants are delicate, you must use two fingers during CPR. The chest needs to return to its normal position after every compression.
Depth of Compressions
During infant CPR, aim for a ventilation rate of around 1 breath every 3 to 5 seconds. This totals approximately 12 to 20 breaths per minute. Make sure that the rescue breath is gentle enough to visibly lift the infant's chest.
Rescue Breathing for Adults
During infant CPR, aim for a ventilation rate of around 1 breath every 3 to 5 seconds. This totals approximately 12 to 20 breaths per minute. Make sure that the rescue breath is gentle enough to visibly lift the infant's chest.
The CPR ratio varies for pregnant individuals, the elderly, and those with medical conditions. So, whether out of hospital or in hospital, recognizing these differences is crucial for providing effective care during cardiac emergencies.
Pregnant Individuals
The recommended compression-to-ventilation ratio is 30:2, similar to that followed in adult CPR. However, rescuers should adjust their hand placement to avoid excessive pressure on the abdomen as the pregnancy advances. It is crucial to ensure the safety of both the pregnant person and the fetus while administering CPR.
Elderly Patients
For elderly patients, CPR follows the same method as for adults, which is the 30:2 compression-to-ventilation ratio. The goal is to provide effective chest compressions and rescue breaths. However, rescuers need to be mindful of the patient's condition or any health issues and adjust the intensity of compressions accordingly.
Patients with Medical or Physical Conditions
Standard CPR guidelines are followed for patients who have a medical or physical condition. Hands-only CPR is recommended, as it helps maintain blood flow and oxygen levels until professional help arrives. The other protocols include promptly recognizing the emergency, seeking help, and performing quality chest compressions.
The CPR ratio serves three key purposes in a cardiac emergency which makes it important:
Proper chest compression ratios help circulate blood, especially to the brain and vital organs.
Using the correct CPR ratio enhances blood circulation and oxygen delivery. This increases the chances of restoring normal breathing and heart function.
Using the correct CPR ratio enhances blood circulation and oxygen delivery. This increases the chances of restoring normal breathing and heart function.
If the CPR ratio is incorrect, it can lead to:
Inadequate compressions can reduce blood circulation to vital organs.
Too few breaths can decrease oxygen levels in the body.
Too many breaths can push air into the stomach instead of the lungs.
The CPR ratio serves three key purposes in a cardiac emergency which makes it important:
Chest compressions continue at the same rate, typically 100-120 per minute, without interruption.
Deliver rescue breaths using a bag-valve mask or mechanical ventilator connected to the advanced airway.
If the CPR ratio is incorrect, it can lead to
The current mandate is based on principles that ensure the right balance between chest compressions and rescue breaths. The 30:2 ratio, as per the mandate, strikes the perfect balance. This ensures oxygen supply and prevents irreversible damage during the attack.
Initially the ratio of chest compression to ventilation was 15:2. Now the standard ratio is 30:2. These changes make CPR easier for bystanders and increase positive patient outcomes.
With the help of practical exercises and feedback mechanisms, CPR training can help individuals develop the skills to deliver proper chest compressions. Training ensures comprehensive understanding and confident application of CPR techniques.
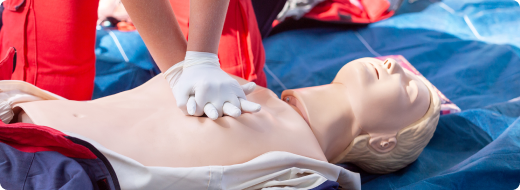
In case of drowning, adjusting the CPR ratio may be necessary because of the nature of the emergency. As drowning often leads to respiratory failure before cardiac arrest, the emphasis is on providing rescue breaths to address the lack of oxygen. Therefore, the CPR ratio may prioritize rescue breaths over chest compressions initially, especially if the victim is not breathing. Once breathing is restored, the standard CPR ratio can be followed.
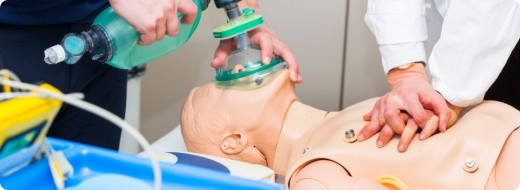
When someone has a tracheostomy or another advanced airway, CPR shifts more toward steady chest compressions. Initially, there’s less emphasis on rescue breaths because the advanced airway helps with breathing. Continuous chest compressions are vital for maintaining blood flow. This reflects our growing understanding of managing airways during CPR, in medical settings.
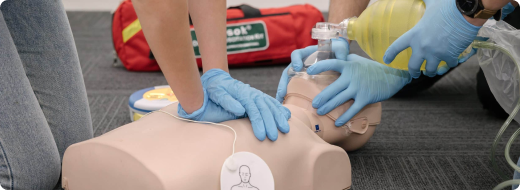
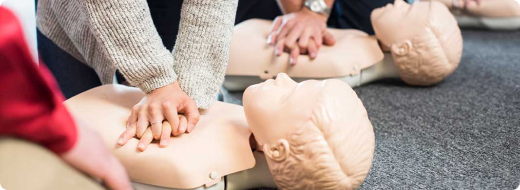
No, the standard 30:2 chest compression to breath ratio for CPR applies in both hypothermia and drug overdose. However, there are key differences in focus. In overdoses, providing the appropriate antidote (like naloxone for opioids) is crucial alongside CPR. For hypothermia, even prolonged CPR efforts might be necessary due to the potential for delayed recovery with rewarming.
Around 180,000–300,000 sudden cardiac deaths occur annually in the United States. Thus, having a CPR Certification ensures you’re skilled in performing CPR with the proper ratio. A CPR course covers life-saving skills, including chest compressions, rescue breaths, AED use, and emergency response techniques. It also covers proper CPR ratios for different age groups and choking relief methods.
The certification exam evaluates your knowledge and practical application of the CPR confirming your readiness to handle real-life emergencies, thus empowering you to save lives.