Online ACLS Course
Get certified with our 100% online ACLS course, designed for medical professionals. Complete it in just 3–4 hours with unlimited quiz retakes, instant certification, and a 2-year validity.
Get certified with our 100% online ACLS course, designed for medical professionals. Complete it in just 3–4 hours with unlimited quiz retakes, instant certification, and a 2-year validity.
| Chapters | 17 |
|---|---|
| CE Credits | 6.0 |
| Validity | 2 Years |
| Cost | $119.00 |
| Duration | 3-4 Hrs |
| ECC | Compliant |
| Exam Attempts | Unlimited |
| Wallet Card | Download/Print/Mail |
When you’re dealing with cardiac emergencies, knowing how the heart works isn’t just helpful; it’s essential. This chapter of your ACLS Certification Course breaks down the heart’s structure and electrical system so you can better understand what’s behind the rhythms you see on a monitor.
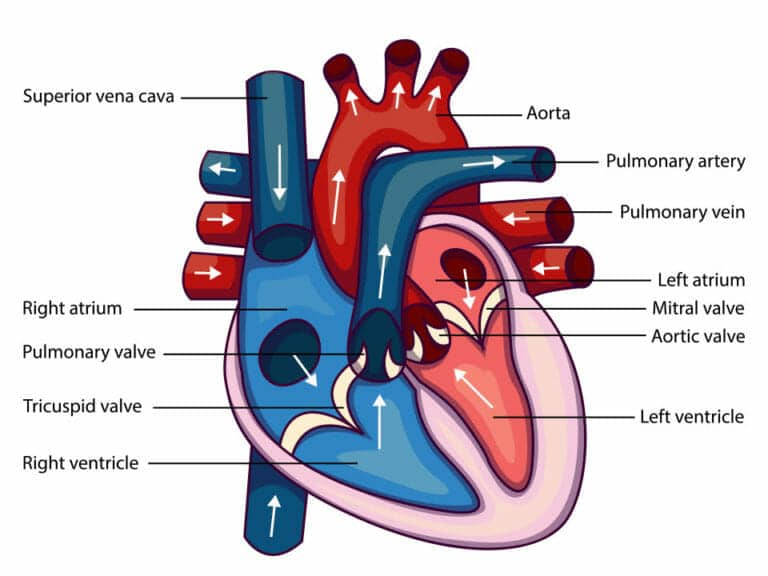
The heart is a hollow muscle with four chambers that work together to keep blood moving through the body.
Here’s how blood flows through the heart:
The cells in the heart muscle can generate and respond to electrical signals without outside input. These impulses make the heart contract.
The signal follows this path:
This entire electrical cycle shows up on an electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG). It’s a common tool used to check how the heart is functioning and to detect possible problems.
An ECG can help:
To read an ECG accurately, it’s important to understand what a normal rhythm looks like.
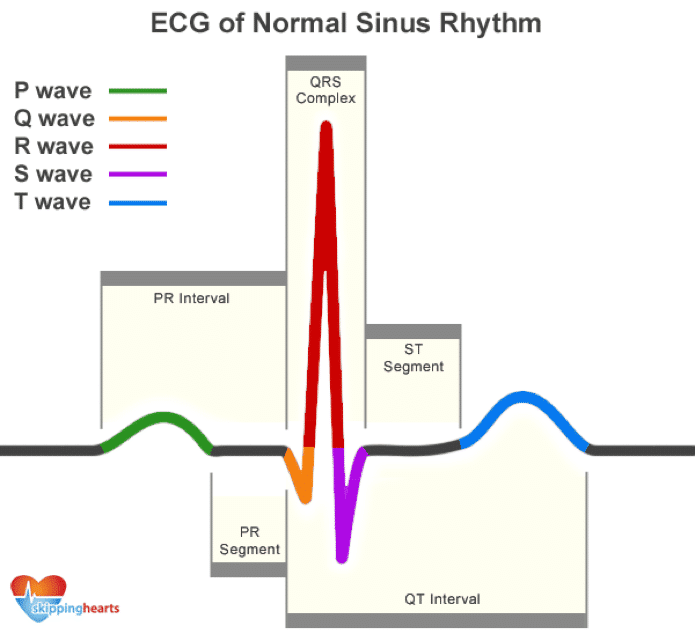
Each heartbeat creates a repeating wave pattern, made up of several parts:
This chapter in your online ACLS course gives you the foundation you’ll need to understand ECG rhythms and respond to cardiac events with confidence.